Présentation
Composants
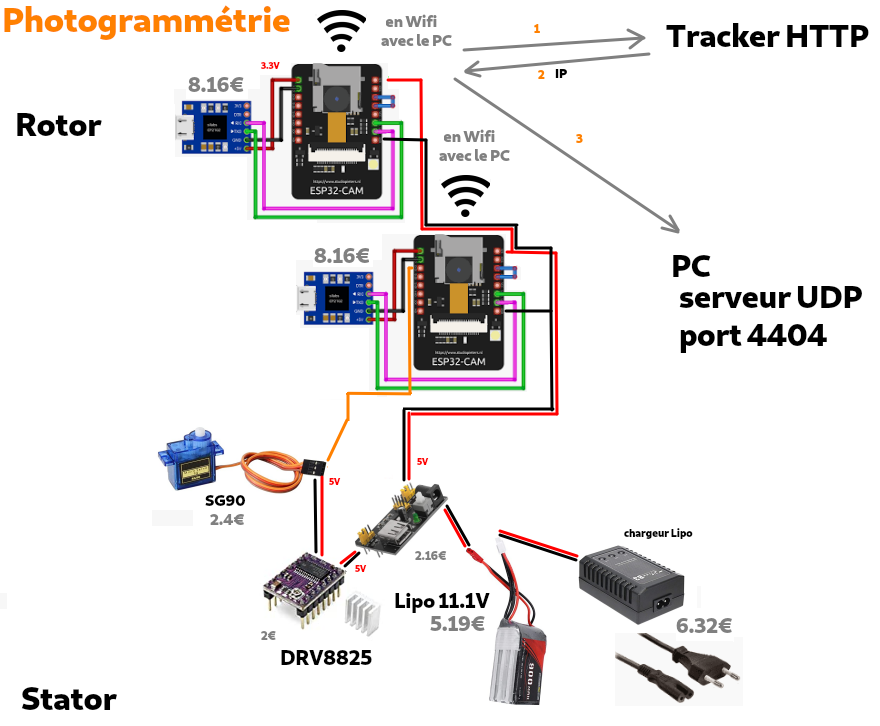
Schéma des composants
Le Code
Logiciel photogrammétrie
Appareil photo tournant et logiciel de photogrammétrie Linux
DESCRIPTION
Vous avez besoin de 3D scanner des objets?
Par exemple une carte mère pour modéliser un nouveau boitier.
En général on pose l'objet sur une table tournante et prend les photos plus ou moins automatiquement.
Or tourner le modèle influe sur les ombres et reflets, donc la table tournante est exclue.
Composants
Stator
Un bras courbé tient deux ESP32-CAM et USB vers TTL.Le serveur crée le modèle PLY en lançant un script shell, (ça prend un moment) et l'uploade, preview three.js
DESCRIPTION
Vous avez besoin de 3D scanner des objets?
Par exemple une carte mère pour modéliser un nouveau boitier.
En général on pose l'objet sur une table tournante et prend les photos plus ou moins automatiquement.
Or tourner le modèle influe sur les ombres et reflets, donc la table tournante est exclue.
Composants
Stator
- L'appareil est alimenté par batterie Lipo 11.1V rechargeable sur une prise 220V sans prise de terre. 1100mA représente 1 ou 2 heures, on verra
- Un convertisseur sort du 5V pour l'ESC et 3.3V pour les ESP.
- Deux USB vers TTL pour uploader le programme sur les ESP
- Un contrôleur de moteur et un servomoteur
Un bras courbé tient deux ESP32-CAM et USB vers TTL.
- Il est monté sur cercle central qui prend l'axe 6mm, a des picots à l'extérieur face vers le bas.
Un pignon ovalisé du servo en faisant un 180° viendra faire défiler les picots.
(pignon ovale et picots en 0.8 c'est plus rapide à imprimer que des engrenages en 0.15)
Le bras a un contrepoids, chaque bras repose sur le bord il tient donc deux roulements M4.
- Lancer le programme serveur sur le PC Linux 64 bits avec beaucoup de RAM.
Ça indique au tracker l'adresse IP du réseal local et ouvre le port UDP 4404. (sinon assigner une IP fixe sur le réseau local) Le serveur est:- un prog GUI avec double preview (FLTK, PHP-TK, GTK, QT? seule certitude:linux),
- une interface web (rafraichir 1 fois par 5 secondes les images écrites),
- ou juste une appli console?
- À l'allumage de l'appareil, deux ESP32-CAM
- initialisent leur caméra
- se connectent au Wifi local puis en TCP:80 au tracker HTTP pour obtenir l'adresse du serveur sur le réseau local
- se connectent en UDP:4404 au serveur du PC.
- Périodiquement
- ils capturent leur image et l'envoient au serveur
- Quand les deux images ont été transférées, le serveur indique aux ESP qu'il faut actionner le moteur. 12 photos 360°: 30° par pas
- Quand 360° ont été effectués, chaque ESP passe en attente de scanner à nouveau.
Tracker HTTP
<?php // si GET['addr'] est renseigné, c'est le serveur qui envoie son IP if(isset($_GET["addr"])){ file_put_contents("ip",$_GET["addr"]); echo 'ok adresse enregistrée'; } // sinon c'est un ESP qui veut savoir l'adresse else echo file_get_contents("ip"); ?>
Serveur sur PC
/* mon API servLib cbx de serveur réseau par multiplexage asynchrone https://c.masta.fr/net/servLib/API.html qui permet d'avoir plusieurs clients sans threads ni fork. */ // getLocalIP() et int a = connectionTCP("www.masta.fr","/tracker.php?addr=..."); 1 ou 0 // peuvent rentrer dans la lib, nettoyée en plus (kick() pas besoin idRequest non plus) // retrouver la source de cette lib #include "servlib.h" int nbClientsConnectes = 0; int client[2]; // sockets. index 0:ESP maître, 1:ESP normal int nbOctetsARecevoir = 0; int nbImagesARecevoir = 0; int id[2]={0,0}; // index image en cours de réception FILE* fp[2]; // le dernier paquet ne fait pas forcément la taille maximale d'un paquet int recu[2]={0,0}; // donc stocke le nombre d'octets de l'image reçus int done[2]={0,0}; // 1 quand un ESP aura envoyé toutes ses images #define CESTBON 1 /*============================================================================*/ void ouvrirFichierEnEcriture(char idf, char idesp){ char fic[16]; sprintf(fic,"dossier/%d-%d.ppm", idf, idesp); fp[n] = fopen(fic,"wb"); } /*============================================================================== Un nouveau client fait une demande d'acceptation Les deux ESP écrivent une image dans le même dossier donc dans le nom du fichier image ils mettent leur index après l'index de la prise de vue dossier/24-0.ppm ESP maître image 24 dossier/24-1.ppm ESP normal image 24 ==============================================================================*/ void onAccept (int idRequest, SOCKET sk) { char n = nbClientsConnectes; ouvrirFichierEnEcriture(id[n], n); client[nbClientsConnectes++] = sk; printf ("ESP %d accepté\n", nbClientsConnectes); // quand les deux sont connectés, leur indique de capturer // L'ESP "maître" fera tourner le plateau après chaque prise if(nbClientsConnectes==2){ cbx_envoyer(client[0],"25",2); //"ESP maître, commence à capturer et m'envoyer 25 images sur 360°" cbx_envoyer(client[1],"25",2); //"ESP normal, commence à capturer et m'envoyer 25 images sur 360°" } } /*============================================================================== Des données arrivent. Un ESP dit au serveur UDP: "tiens voici un paquet de pixels écris-les dans mon fichier actuellement ouvert" ==============================================================================*/ void onData_Arrival (SOCKET sk, char *buf, short nbytes) { //printf("socket %d dit [%s]\n", sk, buf); char n = (sk == client[0]) ? 0 : 1; // ajoute ce paquet au fichier fwrite(fp[n], buf, nbytes); recu[n] += nbytes; // c'est le dernier paquet de l'image? if(recu[n] == nbOctetsARecevoir){ fclose(fp[n]); // ferme le fichier en écriture recu[n]=0; // si c'était pas la dernière image ouvre le prochain en écriture if(id[n]+1 < nbImagesARecevoir) ouvrirFichierEnEcriture(n,id[n]+1); else{ // c'était la dernière image de cet ESP, close(client[n]); // ferme la connection du client done[n] = 1; if(done[0]==1 && done[1]==1) // Les deux ESP ont envoyé leur dernière image system("3d.sh dossier 3d/dossier"); // Faire la Structure From Motion // ensuite le serveur peut fermer cbx_Server_Stop(); // après ça le code poursuit au return 0 du main } id[n]++; } } /*============================================================================== Un client quitte. ==============================================================================*/ void onClient_Left (SOCKET i) { printf("Le socket %d vient de fermer sa connection\n", i); } /*============================================================================== Survient en cas d' erreur inopinée ==============================================================================*/ void onError (SOCKET i, char *errmsg) { printf("%s\n", errmsg); } /*============================================================================== ==============================================================================*/ char* getLocalIP(){ FILE *f; char line[100], *p, *c; int fm = AF_INET; struct ifaddrs *ifaddr, *ifa; int family, s; char* strip = malloc(NI_MAXHOST+1); f = fopen("/proc/net/route", "r"); while(fgets(line, 100, f)){ p = strtok(line, " \t"); c = strtok(NULL, " \t"); if(p!=NULL && c!=NULL){ if(strcmp(c, "00000000") == 0){ //printf("Default interface is : %s \n", p); break; } } } if (getifaddrs(&ifaddr) == -1){ perror("getifaddrs"); return NULL; } //Walk through linked list, maintaining head pointer so we can free list later for (ifa = ifaddr; ifa != NULL; ifa = ifa->ifa_next) { if (ifa->ifa_addr == NULL) continue; family = ifa->ifa_addr->sa_family; if(strcmp( ifa->ifa_name, p) == 0){ if (family == fm) { s = getnameinfo( ifa->ifa_addr, (family == AF_INET) ? sizeof(struct sockaddr_in) : sizeof(struct sockaddr_in6), strip, NI_MAXHOST, NULL, 0, NI_NUMERICHOST); if (s != 0) { printf("getnameinfo() failed: %s\n", gai_strerror(s)); return NULL; } //printf("address: %s", strip); } //printf("\n"); } } freeifaddrs(ifaddr); return strip; } /*============================================================================== ==============================================================================*/ int indiquerMonIPAuTracker(){ SOCKET sk=-1; struct sockaddr_in ServAddr; struct hostent *he; char buf[1024]; char* localip; int n; //printf("gethostbyname(%s)\n", serv); if ((he = gethostbyname(serv)) == NULL) {socket_error("Gethostbyname()"); return -1;} //printf("Socket()\n"); if ((sk = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP)) == INVALID_SOCKET) {socket_error("socket()\n"); return -1;} //printf("fill address\n"); ServAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; ServAddr.sin_port = htons(port); ServAddr.sin_addr = *((struct in_addr *)he->h_addr); //printf("connect()\n"); if (connect(sk, (struct sockaddr*)&ServAddr, sizeof(ServAddr))==-1) { socket_error("connect()"); closesocket(sk); return -1; } // quelle est mon ip sur le réseau Wifi local? localip = getLocalIP(); n = sprintf(buf,"GET /tourelle/tracker.php?addr=%s HTTP/1.1\r\n" "host: %s\r\n\r\n", localip, serv); //printf("%s\n", buf); ecrire(sk, buf, n); free(ip); // le serveur web répond normalement en PHP 'ok adresse enregistrée' n = recv(sk, buf, sizeof(buf), 0); //buf[n]=0; //printf("\n%s\n", buf); close(sk); // regarde en-tête HTTP: 200 OK? // si pas 200 Ok le signaler if (buf[9]=='2' && buf[10]=='0' && buf[11]=='0' && buf[12]==' ' && buf[13]=='O' && buf[14]=='K') return CESTBON; return 0; } /*============================================================================== Point d'entrée ==============================================================================*/ int main(){ // indique au tracker HTTP mon IP sur le réseau local if(indiquerMonIPAuTracker() != CESTBON){ printf("souci: serveur ne dit pas 200 OK\n"); return 1; } // Démarre un serveur UDP sur le port 4404 pour 2 clients maximum // Part dans une boucle infinie qui déclenche les callbacks ci-dessus // jusqu'à ce que cbx_Server_Stop() soit invoquée cbx_server_start(UDP,4404,2); printf("exited gracefully\n"); return 0; }
Le programme ESP32 "Maître" dirige le servomoteur
#include <ESP32Servo.h> Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo // 16 servo objects can be created on the ESP32 int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position // sur le schéma le servo va au pin GPIO 12 int servoPin = 12; void setup() { // Allow allocation of all timers ESP32PWM::allocateTimer(0); ESP32PWM::allocateTimer(1); ESP32PWM::allocateTimer(2); ESP32PWM::allocateTimer(3); myservo.setPeriodHertz(50); // standard 50 hz servo myservo.attach(servoPin, 500, 2400); // attaches the servo on pin 18 to the servo object // using default min/max of 1000us and 2000us // different servos may require different min/max settings // for an accurate 0 to 180 sweep } void loop() { for (pos = 0; pos <= 180; pos += 1) { // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees // in steps of 1 degree myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos' delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position } for (pos = 180; pos >= 0; pos -= 1) { // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos' delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position } }
Un ESP32 obtient l'IP du serveur via une requête HTTP
//https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/blob/master/sockets/client/socketClient.c #include <string.h> #include <WiFi.h> //include <esp_log.h> //include <freertos/FreeRTOS.h> //include <freertos/task.h> #include <lwip/sockets.h> //include "sdkconfig.h" #include <esp_camera.h> int sk; short nbImagesAEnvoyer; // le serveur indique combien d'images il veut short imagesEnvoyees = 0; /*============================================================================*/ void initCamera(){ } /*============================================================================*/ char connectionAuWifi(){ const char* ssid = "LiveBoxssid"; const char* mdp = "12345"; wl_status_t status; WiFi.begin(ssid, mdp); Serial.print("Connection au Wifi "); while(1){ status = WiFi.status(); if (status == WL_NO_SSID_AVAIL){ Serial.println("SSID introuvable"); break; } else if(status == WL_CONNECTED){ Serial.println("Connection Wifi établie"); break; } else if(status == WL_CONNECT_FAILED){ Serial.println("Mot de passe KO"); break; } //Serial.print("."); // il y a une led du flash sur l'ESP digitalWrite(PORT_LED_FLASH, HIGH); delay(100); digitalWrite(PORT_LED_FLASH, LOW); delay(500); } Serial.print("\n"); } /*============================================================================*/ char* connectionTrackerHTTP() { struct sockaddr_in serverAddr; struct hostent *he; char* serv = "www.masta.fr"; char requeteHTTP[100]; char* ip; int n; sk = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP); if ((he = gethostbyname(serv)) == NULL) { Serial.println("Gethostbyname()"); return NULL;} if ((sk = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP)) == INVALID_SOCKET) {Serial.println("Gethostbyname()"); return NULL;} ServAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; ServAddr.sin_port = htons(80); ServAddr.sin_addr = *((struct in_addr *)he->h_addr); n = connect(sk, (struct sockaddr *)&serverAddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); n = sprintf(requeteHTTP,"GET /tourelle/tracker.php HTTP/1.1\nhost:%s", serv); n = send(sk, requeteHTTP, strlen(requeteHTTP), 0); ip = malloc(16); n = recv(sk, ip, 15, 0); ip[n]=0; close(sk); return ip; } /*============================================================================*/ // mettre UDP void seConnecterAuserveur(char* ip){ sk = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP); struct sockaddr_in serverAddress; serverAddress.sin_family = AF_INET; inet_pton(AF_INET, ip, &serverAddress.sin_addr.s_addr); serverAddress.sin_port = htons(80); int n = connect(sk, (struct sockaddr *)&serverAddress, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); char buf[4]; n = recv(sk, buf, 3, 0); buf[n]=0; nbImagesAEnvoyer = atoi(buf); } /*============================================================================*/ void setup(){ initCamera(); char* ip = connectionTrackerHTTP(); if(ip) seConnecterAuserveur(ip); } /*============================================================================*/ void loop(){ // tant que n < nbImagesAEnvoyer while (imagesEnvoyees++ < nbImagesAEnvoyer){ // prendre image // envoyer image send(sk,buf,sizeof(buf)); } close(sk); } /* int create_ipv4_socket() { struct addrinfo hints; struct addrinfo *res; struct in_addr *addr; hints.ai_family = AF_INET; hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; int err = getaddrinfo(UDP_IPV4_ADDR, TCP_PORT, &hints, &res); if(err != 0 || res == NULL) { printf("DNS lookup failed err=%d res=%p\n", err, res); return -1; } / * Code to print the resolved IP. Note: inet_ntoa is non-reentrant, look at ipaddr_ntoa_r for "real" code * / addr = &((struct sockaddr_in *)res->ai_addr)->sin_addr; printf("DNS lookup succeeded. IP=%s\n", inet_ntoa(*addr)); l_sock = socket(res->ai_family, res->ai_socktype, 0); if(l_sock < 0) { printf("... Failed to allocate socket.\n"); freeaddrinfo(res); return -1; } struct timeval to; to.tv_sec = 2; to.tv_usec = 0; setsockopt(l_sock,SOL_SOCKET,SO_SNDTIMEO,&to,sizeof(to)); if(connect(l_sock, res->ai_addr, res->ai_addrlen) != 0) { printf("... socket connect failed errno=%d\n", errno); close(l_sock); freeaddrinfo(res); return -1; } printf("... connected\n"); freeaddrinfo(res); // All set, socket is configured for sending and receiving return l_sock; } */
Un mot sur les photos:
Après en avoir tenté d'installer 13 logiciels sans succès, le premier qui a fonctionné est SMVS. Il fonctionne tout CPU sans CUDA.
Github
Un tutoriel qui fonctionne
Installation
Premier modèle 3D, à la main
Ensuite visualisation et réduction du modèle ply dans Meshlab, export en STL, 3ds, obj.
- Prendre le sujet en entier, il doit être entièrement sur chaque photo
- Prendre le moins de photos possible, mais pas trop peu. Le meilleur rendu est fait non pas avec 2000 photos mais avec une dizaine de photos à une hauteur, et une dizaine d'autres photos prises d'un peu plus haut.
- La lumière doit être diffuse, aucune ombre.
- Supprimer toute image floue.
Après en avoir tenté d'installer 13 logiciels sans succès, le premier qui a fonctionné est SMVS. Il fonctionne tout CPU sans CUDA.
Github
Un tutoriel qui fonctionne
Installation
$ git clone https://github.com/simonfuhrmann/mve.git $ git clone https://github.com/flanggut/smvs.git $ make mve $ make smvsOn peut trouver quelques sets d'images sur le net (Regard3D), cependant à ce stade il ne faut pas hésiter à prendre ses propres photos.
Premier modèle 3D, à la main
# ça crée un dossier test $ ./mve/apps/makescene/makescene -i kermit test Makescene (built on Oct 12 2020, 02:29:56) Found 14 directory entries. Creating output directories... Importing image: IMG_3472.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0000.mve... Importing image: IMG_3473.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0001.mve... Importing image: IMG_3474.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0002.mve... Importing image: IMG_3475.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0003.mve... Importing image: IMG_3476.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0004.mve... Importing image: IMG_3477.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0005.mve... Importing image: IMG_3478.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0006.mve... Importing image: IMG_3479.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0007.mve... Importing image: IMG_3480.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0008.mve... Importing image: IMG_3481.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0009.mve... Importing image: IMG_3482.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0010.mve... Importing image: IMG_3483.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0011.mve... Importing image: IMG_3484.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0012.mve... Importing image: IMG_3485.JPG, writing MVE view: view_0013.mve... Imported 14 input images, took 754 ms. # 2/5 Structure From Motion reconstruction. crée dossiers .mve $ ./mve/apps/sfmrecon/sfmrecon test # 3/5 SMVS (Shading-aware Multi-view Stereo) reconstruction # Là ça pompe la RAM # 500Mo de RAM et 100% CPU pendant longtemps $ ./smvs/app/smvsrecon test # 4/5 FSS Floating Scale Surface Reconstruction (crée le mesh) $ ./mve/apps/fssrecon test/smvs-B0.ply test/smvs-surface.ply #mettre -p100 pour kermit $ ./mve/apps/meshclean -p10 test/smvs-surface.ply test/smvs-clean.plyMon script shell qui permet de créer un modèle en une seule ligne de commande
$ chmod +x 3d.sh $ ./3d.sh imagesets/kermit 3d/kermit
#/bin/bash # ./3d.sh dossierimages dossierfinal echo "1/5 makescene ..." ./mve/apps/makescene/makescene -i $1 $2 echo "2/5 Structure From Motion reconstruction ..." ./mve/apps/sfmrecon/sfmrecon $2 # lui pompe CPU et RAM echo "3/5 SMVS (Shading-aware Multi-view Stereo) reconstruction ..." ./smvs/app/smvsrecon $2 echo "4/5 FSS Floating Scale Surface Reconstruction ..." if -f "$2/smvs-B0.ply"; then echo "B0 ..." ./mve/apps/fssrecon/fssrecon $2/smvs-B1.ply $2/smvs-surface.ply fi if -f "$2/smvs-B1.ply"; then echo "B1 ..." ./mve/apps/fssrecon/fssrecon $2/smvs-B1.ply $2/smvs-surface.ply fi #./mve/apps/fssrecon/fssrecon test/smvs-[B,S].ply test/smvs-surface.ply echo "5/5 meshclean ..." ./mve/apps/meshclean/meshclean -p10 $2/smvs-surface.ply $2/smvs-clean.plyCe script peut être lancé automatiquement dès que la dernière image est reçue.
Ensuite visualisation et réduction du modèle ply dans Meshlab, export en STL, 3ds, obj.